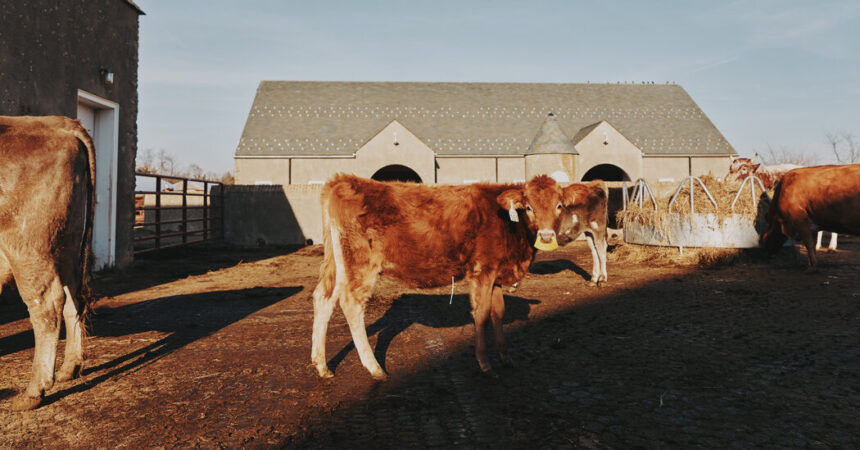
A minimum of one particular person in Texas has been identified with chook flu following contact with dairy cows presumed to be contaminated, state officers mentioned on Monday.
The announcement provides a worrying dimension to an outbreak that has affected hundreds of thousands of birds and sea mammals worldwide and, most not too long ago, cows in america.
To date, there aren’t any indicators that the virus has advanced in ways in which would assist it unfold extra simply amongst individuals, federal officers have mentioned.
The affected person’s major symptom was conjunctivitis; the person is being handled with an antiviral drug and is recovering, in response to the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention.
The Division of Agriculture introduced the primary instances in dairy herds in Texas and Kansas final week, after which, just a few days later, in an extra herd in Michigan. Preliminary testing means that cows in New Mexico and Idaho can also be contaminated.
The virus has been recognized as the identical model of H5N1, an influenza subtype, that’s circulating in North American birds.
The C.D.C. is working with state well being departments to watch others who could have been involved with contaminated birds and animals, the company mentioned on Monday.
That is solely the second case of H5N1 chook flu in individuals in america; the primary was in 2022. Specialists mentioned that they consider the danger to most people stays low. However testing and evaluation is ongoing, and there are various unanswered questions.
“It is a quickly evolving state of affairs,” the usD.A. mentioned in its announcement final week.
Right here’s what to know:
What’s chook flu?
Fowl flu, or avian influenza, is a bunch of flu viruses which can be primarily tailored to birds. The actual virus in these new instances, known as H5N1, was first recognized in 1996 in geese in China, and in individuals in Hong Kong in 1997.
In 2020, a brand new, extremely pathogenic type of H5N1 emerged in Europe and unfold rapidly world wide. In america, it has affected greater than 82 million farmed birds, the worst chook flu outbreak in U.S. historical past.
Because the virus was first recognized, there have additionally been sporadic instances in individuals in different international locations. In 2023, there have been 248 instances of individuals contaminated with H5N1 virus, and 139 deaths, in response to the World Well being Group. However a overwhelming majority resulted from extended, direct contact with birds.
H5N1 doesn’t but appear to have tailored to unfold effectively amongst individuals, consultants say.
How did cows get chook flu?
Cows weren’t considered a species at excessive danger.
“The truth that they’re vulnerable — the virus can replicate, could make them sick — that’s one thing I wouldn’t have predicted,” mentioned Richard Webby, an influenza virologist at St. Jude Youngsters’s Analysis Hospital.
However earlier this yr, experiences of sick cows started rising in Texas and New Mexico. Lifeless birds had been additionally discovered on a few of these farms, and laboratory testing finally confirmed the cows had been contaminated with chook flu.
There are a selection of ways in which the virus may need discovered its means into cattle. The most certainly route, a number of consultants mentioned, is that contaminated wild birds, which shed the virus of their feces and oral secretions, contaminated the cows’ meals or water.
However different free-ranging animals identified to be vulnerable to the virus, resembling cats and raccoons, might even have introduced the virus onto dairy farms.
How have cows been affected?
Though the virus is commonly deadly in birds, it seems to be inflicting comparatively gentle sickness in cows.
“It’s not killing animals, and so they appear to be recovering,” mentioned Dr. Joe Armstrong, a veterinarian and cattle manufacturing knowledgeable on the College of Minnesota Extension. Final week, the usD.A. mentioned that there have been no plans to “depopulate,” or kill, affected herds, which is the usual process when poultry flocks are contaminated with the virus.
The illness is primarily affecting older cows, which have developed signs that embody a lack of urge for food, a low-grade fever and a major drop in milk manufacturing. The milk that the cows do produce is commonly “thick and discolored,” in response to Texas officers. The virus has additionally been present in unpasteurized milk samples collected from sick cows.
It isn’t but clear whether or not the chook flu virus is the only reason behind all the signs and sicknesses which were reported, consultants cautioned.
How widespread is the issue?
It’s unclear. As of final Friday, the usD.A.’s Nationwide Veterinary Companies Laboratory had confirmed chook flu infections in two herds in Texas, two herds in Kansas and one herd in Michigan. Preliminary testing has advised that further herds in Texas, New Mexico and Idaho can also have the virus, however these findings haven’t but been confirmed by the nationwide laboratory. To date, it has been discovered solely in dairy cows and never in beef cattle.
However as a result of cows aren’t routinely examined for chook flu, and the sickness has been comparatively gentle, there may very well be different contaminated herds which have escaped detection, consultants mentioned.
And the motion of cattle between states might transport the virus to new places. The affected dairy in Michigan had not too long ago imported cows from one of many contaminated Texas herds. On the time the cows had been transported, the animals weren’t displaying any signs. The farm in Idaho had additionally not too long ago imported cows from an affected state, Idaho officers mentioned.
How is it spreading?
That may be a key, and nonetheless unanswered, query. It’s potential that the contaminated cows are all choosing up the virus independently, particularly if shared meals or water sources have been contaminated.
A extra worrisome risk, nevertheless, is that the virus is spreading from cow to cow. On Friday, the usD.A. famous that “transmission between cattle can’t be dominated out.”
A number of scientists mentioned that they might be shocked if there was not a point of cow-to-cow transmission. “How else might it transfer so quickly?” mentioned Dr. Gregory Grey, an infectious illness epidemiologist on the College of Texas Medical Department.
If the virus seems to unfold simply between cows, that might result in bigger, extra sustained outbreaks. It could additionally give the virus extra alternatives to adapt to its new mammalian hosts, rising the danger that it acquires mutations that make it extra harmful to individuals.
How will officers know if chook flu adapts to unfold between individuals?
Analyzing the genetic sequence of the virus from contaminated birds, cows and folks can reveal whether or not H5N1 has acquired mutations that assist it unfold amongst individuals.
Scientists have been carefully monitoring infections in birds and sea mammals and, now, cows. To date, the virus doesn’t appear to have gained the power to unfold effectively between individuals.
In 2012, scientists confirmed that H5N1 was in a position to unfold by air between ferrets — a preferred mannequin for finding out transmission of respiratory viruses amongst individuals — after buying 5 mutations.
A pattern of chook flu remoted from a Chilean man final yr had two mutations that point out adaptation to infecting mammals. However these mutations have beforehand been seen with out the virus evolving additional to unfold between individuals, consultants mentioned.